All News

Phys.org / Stony coral tissue loss disease is shifting the ecological balance of Caribbean reefs
The outbreak of a deadly disease called stony coral tissue loss disease is destroying susceptible species of coral in the Caribbean while helping other, "weedier" organisms thrive—at least for now—according to a new study ...

Phys.org / Call of the conch: Archaeologists suggest Indigenous Americans used sound to organize local communities
Archaeologists have modeled the auditory range of conch-shell trumpets in the 9th–11th century US Southwest, proposing that the sound was key in the structuring of pre-Columbian Pueblo communities.

Phys.org / Rising mercury levels may contribute to declining Steller sea lion populations
A team of researchers from Texas A&M University and other institutions has made a surprising discovery about rising mercury levels in Steller sea lion pups that may have detrimental effects on the endangered species.
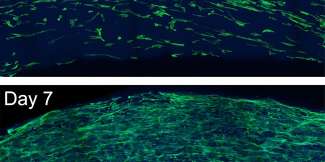
Phys.org / Aligned peptide 'noodles' could enable lab-grown biological tissues
A team of chemists and bioengineers at Rice University and the University of Houston have achieved a significant milestone in their work to create a biomaterial that can be used to grow biological tissues outside the human ...
Medical Xpress / Newly discovered mechanism of T-cell control can interfere with cancer immunotherapies
Activated T cells that carry a certain marker protein on their surface are controlled by natural killer (NK) cells, another cell type of the immune system. In this way, the body presumably curbs destructive immune reactions.
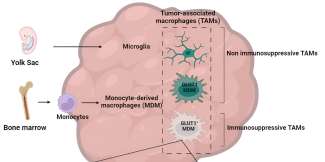
Medical Xpress / Scientists discover new immunosuppressive mechanism in brain cancer
The Wistar Institute assistant professor Filippo Veglia, Ph.D., and team, have discovered a key mechanism of how glioblastoma—a serious and often fatal brain cancer—suppresses the immune system so that the tumor can grow ...

Phys.org / Research discovers plants utilize drought stress hormone to block snacking spider mites
Recent findings that plants employ a drought-survival mechanism to also defend against nutrient-sucking pests could inform future crop breeding programs aimed at achieving better broadscale pest control.

Phys.org / Tweaking isotopes sheds light on promising approach to engineer semiconductors
Research led by scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has demonstrated that small changes in the isotopic content of thin semiconductor materials can influence their optical and electronic ...
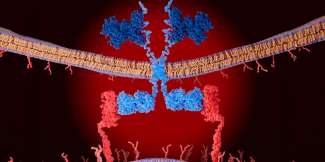
Medical Xpress / Pan-cancer analysis uncovers a new class of promising CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets
Targeting anti-cancer therapy to affect cancer cells but not healthy cells is challenging. For chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy, where a patient's own immune cells are re-engineered to attack cancer ...
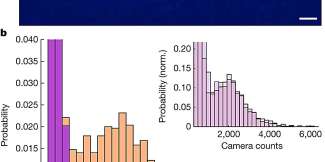
Phys.org / Physicists create an optical tweezer array of individual polyatomic molecules for the first time
A team of physicists at Harvard University has succeeded in trapping individual polyatomic molecules in optical tweezer arrays for the first time. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how they ...

Medical Xpress / Largest quantitative synthesis to date reveals what predicts human behavior and how to change it
Pandemics, global warming, and rampant gun violence are all clear lessons in the need to move large groups of people to change their behavior. When a crisis hits, researchers, policymakers, health officials, and community ...

Phys.org / Chemist explores the real-world science of Star Wars
A professor at the University of Warwick is exploring the chemistry of the galaxy far, far away this Star Wars Day, May the 4th.