Best of Last Week—Boat hitting shark recorded, realistic rendering of fabrics, tiny heart deletions linked to AFib
It was a busy week for oceanic biology research as a small team of marine biologists from the U.S. and Ireland recorded the first-ever images and data of a shark being struck by a boat—the seven-meter-long basking shark was struck by a boat and its fate is unknown. Also, another team, this one with members from Oregon State University, made the first scientific confirmation in Puget Sound of two distinct shark species, one of them critically endangered. The sightings may indicate that sharks are adjusting to environmental changes. And a combined team of marine researchers from the University of Rhode Island and Nova Southeastern University in Florida found that a 26-foot whale shark made consistent migrations over four years of tracking.
In technology news, a combined team of AI researchers from Shandong and Nanjing universities used a lightweight neural network to enable realistic rendering of woven fabrics in real time. And a team of chemical engineers at MIT produced hydrogen by exposing aluminum soda cans to sea water—they subsequently sped up the process by adding caffeine. Meanwhile, an international team of scientists published a commentary piece in the journal Joule warning against giving in to the hype surrounding the development of green hydrogen from direct seawater electrolysis—they suggest a realistic approach is still years away. And a combined team of machine-learning researchers from MIT and Northeastern University found that allocating scarce resources with AI randomization can improve fairness.
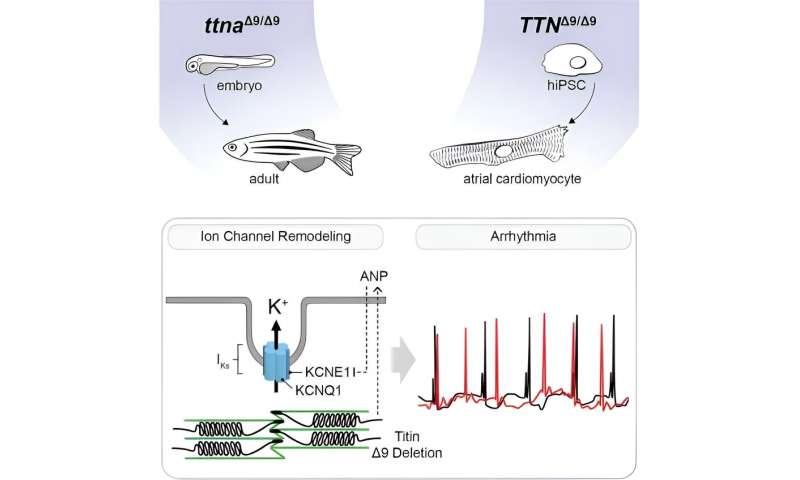
In other news, a team of medical researchers affiliated with several institutions in Canada conducted a study showing no association between moderate alcohol consumption and a longer life—prior studies finding such a link were flawed. A team at NASA reported that a rock on Mars found by the Perseverance rover contains potential evidence of life. And finally, a combined team of medical researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the University of Illinois Chicago found a link between tiny deletions in heart muscle protein in baby zebrafish and human heart tissue and long-term effects on adult atrial fibrillation.
© 2024 Science X Network