Phys.org news

Phys.org / Researchers observe a large anomalous Hall effect triggered by spin-fluctuating devil's staircase
A research group from University of Tsukuba has discovered that fluctuations of electron spins in magnetic materials trigger a large anomalous Hall effect during phase transition known as the devil's staircase magnetic transition.

Phys.org / Team of biologists discover fluorescence in 27 marine creatures
A team of zoologists and marine biologists affiliated with several institutions in Indonesia, working with a colleague from Germany, has discovered previously unknown instances of fluorescence in 27 marine creatures.

Phys.org / New technique achieves visualization of instantaneous states of materials in high-speed devices
Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed an ultrafast time-resolved scanning electron microscopy instrument by integrating a scanning electron microscope with a femtosecond laser. This innovative system facilitates ...

Phys.org / Backdoor method creates high-entropy material at lower temperatures
Entropy is a hot mess. Randomness and disorder are not exactly virtues in science. Yet it turns out, a sloppy jumble of differently sized atoms can do a better job stabilizing certain nanocrystals than a tidy arrangement ...
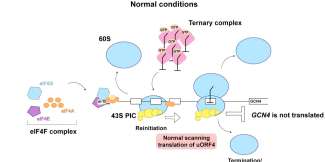
Phys.org / Biologists take closer look at stress response in cells
A new study from the Zaher Lab at Washington University in St. Louis, published in Molecular Cell, dives into the mechanisms behind the ways cells respond to stress.

Phys.org / Study suggests at-camera gaze can increase scores in simulated interviews
Eye-contact has a significant impact on interpersonal evaluation, and online job interviews are no exception. In addition to the quality of a resume, the direction of the interviewee's gaze might help (or hinder) their chances ...

Phys.org / Scientists use tyrosine nanomedicine to halt melanoma growth
An international research team used a common amino acid, tyrosine, packaged as a nanomedicine, to change the metabolism of melanoma, a deadly skin cancer, and prevent cancer growth.

Phys.org / Simple tool could facilitate discovery of new mechanically-responsive materials
The exploration of mechanophores continues to expand the practical application of these molecules in materials science, organic synthesis, and pharmaceuticals due to their ability to change physically or chemically in response ...

Phys.org / Marsquakes could reveal whether liquid water exists underground on red planet
If liquid water exists today on Mars, it may be too deep underground to detect with traditional methods used on Earth. But listening to earthquakes that occur on Mars—or marsquakes—could offer a new tool in the search, ...

Phys.org / Antifreeze proteins show promise for organ preservation
Cryogenic damage has long presented a significant barrier to effective organ preservation, posing challenges to advancements in transplantation and medical treatments. The formation of ice crystals during freezing can compromise ...

Phys.org / City sprawl is now large enough to sway global warming over land
Just how much heat does city sprawl add to large-scale warming? That's one longstanding question researchers sought to answer in a new study recently published in the journal One Earth.

Phys.org / In the hunt for a second Earth, look to small planets, says new research
Scientists around the world are constantly on the hunt for planets outside our solar system that could potentially provide a habitable environment for life.