Dentures made with 3-D printing technology
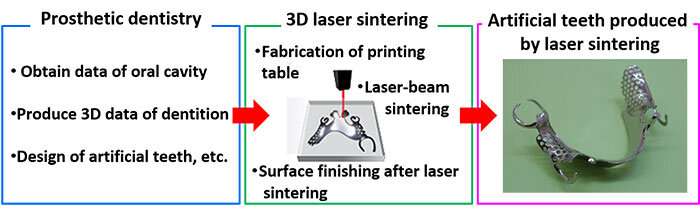
AIST and IDS Co., Ltd. have jointly developed technology that enables the production of artificial teeth using 3-D printing technology and obtained pharmaceutical regulatory approval for the use of a cobalt-chromium alloy powder.
The production of partial dentures by the current cutting process takes a long time and offers poor material yield. Furthermore, many dental technicians in Japan are reaching retirement age, resulting in shortage of skilled workers in the industry. To make dental manufacturing more appealing, the researchers aimed to achieve the practical use of artificial teeth made by additive manufacturing utilizing 3-D printing, which can reduce costs and the number of processes by adopting the latest technologies.
With the aim of accelerating the development of dental prostheses, AIST served as a secretariat to produce and publish "Guidelines for Development of Dental Prosthetic Devices Using 3-D Additive Manufacturing Technology." On the basis of these guidelines, IDS Co., Ltd. applied for pharmaceutical regulatory approval of a cobalt-chrome alloy powder, and AIST researched the microstructure of additive manufacturing material, as well as the effects of the powder size and layering direction on durability, to determine the conditions necessary for practical use.
The researchers aim to make dental prostheses produced by additive manufacturing technology covered by the health insurance system of Japan. They also aim to obtain approval for a domestically produced powder of cobalt-chrome alloy. Furthermore, they aim to develop artificial teeth made of titanium for patients with allergies.
Provided by Advanced Industrial Science and Technology