Distinct molecular subtypes associated with prognosis and androgen response in patients with prostate cancer
Cellular senescence has been considered a hallmark of aging. The authors of a new publication in Acta Materia Medica aimed to establish two novel prognostic subtypes for prostate cancer patients using senescence-related lncRNAs.
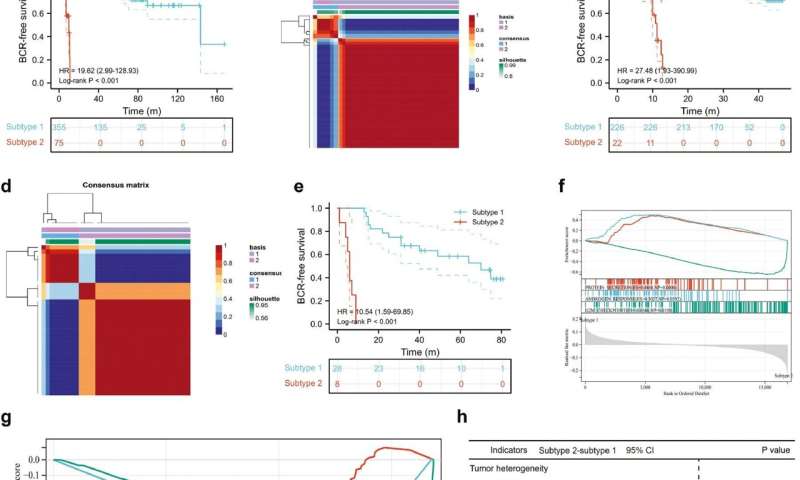
A nonnegative matrix factorization algorithm was used to identify molecular subtypes. Analyses were completed using software R 3.6.3 and its suitable packages. Using SNHG1, MIAT and SNHG3, 430 patients in TCGA database were classified into two subtypes associated with biochemical recurrence (BCR)-free survival and subtype 2 was prone to BCR (HR: 19.62, p < 0.001).
Similar results were observed in GSE46602 and GSE116918. For hallmark gene set enrichment, it was found that protein secretion and androgen response were highly enriched in subtype 1 and G2M checkpoint was highly enriched in subtype 2.
For tumor heterogeneity and stemness, homologous recombination deficiency and tumor mutation burden were significantly higher in subtype 2 than subtype 1. The top 10 genes between subtype 2 and subtype 1 were CUBN, DNAH9, PTCHD4, NOD1, ARFGEF1, HRAS, PYHIN1, ARHGEF2, MYOM1 and ITGB6 with statistical significance.
In terms of immune checkpoints, only CD47 was significantly higher in subtype 1 than that in subtype 2. For the overall assessment, no significant difference was detected between two subtypes, while B cells score was significantly higher in subtype 1 than subtype 2.
Overall, two distinct subtypes closely associated with BCR-free survival and androgen response for prostate cancer were found. These subtypes might facilitate future research in the field of prostate cancer.
More information:
Dechao Feng et al, Senescence-associated lncRNAs indicate distinct molecular subtypes associated with prognosis and androgen response in patients with patients with prostate cancer, Acta Materia Medica (2023). DOI: 10.15212/AMM-2023-0025
Provided by Compuscript Ltd