Aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides as a novel class of immunomodulators with interleukin-17A inhibitory activity
A new article published in Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B discusses aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides as a novel class of immunomodulators with interleukin-17A inhibitory activity.
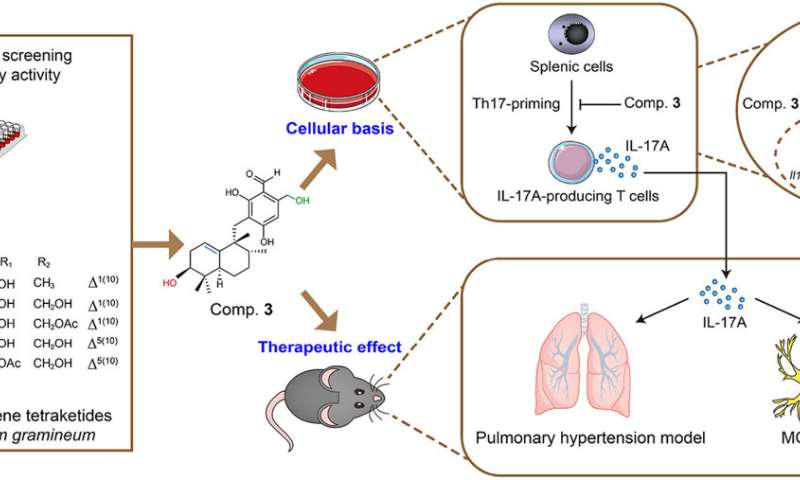
Interleukin (IL)-17A, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, is a fundamental function in the onset and advancement of multiple immune diseases. To uncover the primary compounds with IL-17A inhibitory activity, a large-scale screening of the library of traditional Chinese medicine constituents and microbial secondary metabolites was conducted using splenic cells from IL-17A-GFP reporter mice cultured under Th17-priming conditions.
The results indicated that some aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides isolated from a wetland mud-derived fungus, Myrothecium gramineum, showed remarkable IL-17A inhibitory activity. Nine new aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides, myrogramins A–I (1, 4–11), and two known ones (2 and 3) were isolated and identified from the strain.
Compounds 1, 3, 4, 10, and 11 exhibited significant IL-17A inhibitory activity. Among them, compound 3, with a high fermentation yield dose-dependently inhibited the generation of IL-17A and suppressed glycolysis in splenic cells under Th17-priming conditions. Strikingly, compound 3 suppressed immunopathology in both IL-17A-mediated animal models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and pulmonary hypertension.
The results revealed that aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides are a novel class of immunomodulators with IL-17A inhibitory activity, and hold great promise applications in treating IL-17A-mediated immune diseases.
More information:
Xin Tang et al, Aureane-type sesquiterpene tetraketides as a novel class of immunomodulators with interleukin-17A inhibitory activity, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.017
Provided by Compuscript Ltd