Prognostic value and immune infiltration analyses of cuproptosis-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma
The role of cuproptosis, a newly discovered form of programmed cell death, remains poorly understood in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
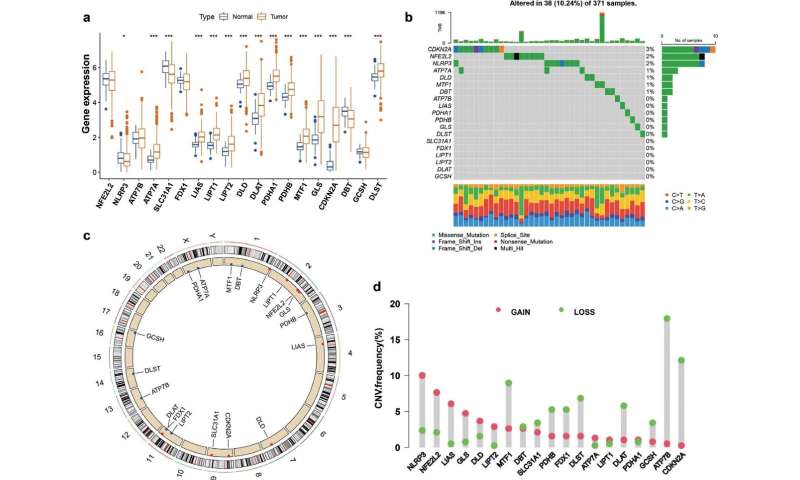
Published in Acta Materia Medica, this study described by this article was aimed at constructing a novel cuproptosis model for analyzing the clinical features, mutation characteristics and immune profile of HCC associated with cuproptosis-related genes (CRG), and to analyze the prognostic value of CRGs in HCC.
We comprehensively evaluated HCC datasets containing clinicopathological information from The Cancer Genome Atlas and GEO, on the basis of 19 CRGs. The prognostic value of the cuproptosis-related risk score was established.
The results revealed two clusters associated with cuproptosis. Cluster B exhibited pronounced isolated innate immune cell infiltration and poor prognosis, and significant differences in prognosis and immune infiltration were observed between the groups with high and low cuproptosis risk.
High copper mortality risk scores were associated with an elevated tumor mutational burden (TMB) and poor prognosis. The findings suggest that evaluating copper-death subtypes provides insights into CRGs. Moreover, the copper mortality risk score model aids in characterizing prognosis and immune infiltration independently of the TMB.
More information:
Junjie Li et al, Prognostic value and immune infiltration analyses of cuproptosis-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma, Acta Materia Medica (2023). DOI: 10.15212/AMM-2023-0035
Provided by Compuscript Ltd