Stable PbS colloidal quantum dot inks enable scalable preparation of infrared solar cells by blade coating
Developing clean and low-cost solar photovoltaic power is an important strategy for achieving carbon neutrality.
Theoretical research shows that a tandem device consisting of a 1.55 eV perovskite top-cell and 1.0 eV PbS quantum dots (QDs) bottom-cell can achieve an ideal power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 43%, which is much higher than the 33% single junction limit. Thus, 1.0 eV QD near-infrared solar cells (NIRSCs) show high potential in next-generation photovoltaics and tandem solar cells.
Researchers led by Prof. Haisheng Song at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), China, are interested in next generation photovoltaic technology such as QDs NIRSCs. The work, titled "Stable PbS colloidal quantum dot inks enable blade-coating infrared solar cells," was published in Frontiers of Optoelectronics.
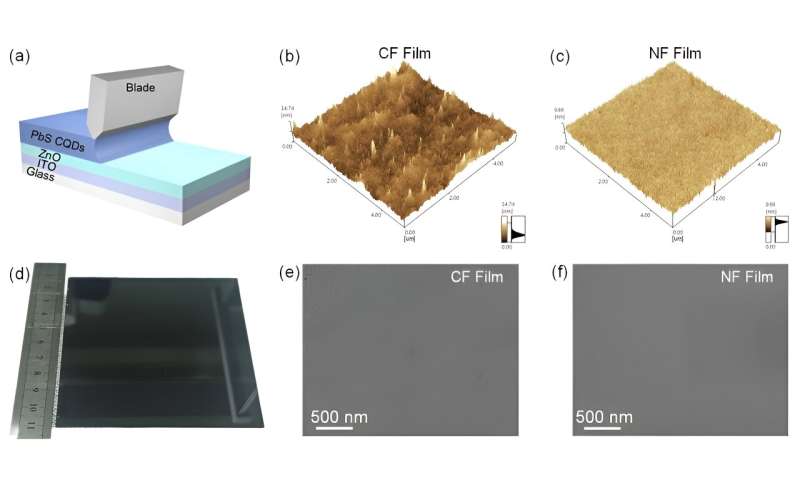
Until now, such devices suffered from the absence of scalable preparation method for device fabrication. Thus, the researchers developed a mixed solvent system from dimethylformamide (DMF) and butylamine (BTA) according to Lewis acid-base theory and DLVO theory. This system can maintain the stability of QD inks and is compatible with the large-scale blade coating process.
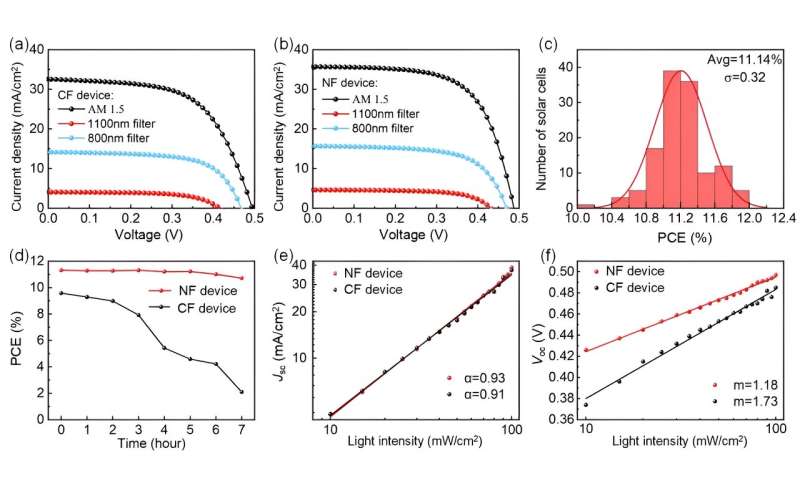
The large area QD film based device achieves an average PCE of 11.14% and an 800 nm-filtered PCE of 4.28%, which are the top values reached in reported research literature to date for the blade coating method.
More information:
Xinzhao Zhao et al, Stable PbS colloidal quantum dot inks enable blade-coating infrared solar cells, Frontiers of Optoelectronics (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s12200-023-00085-0
Provided by Frontiers Journals