Auxin response factor genes identified in Arabian jasmine
A new study in the Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science identifies auxin response factor genes in Arabian jasmine.
Auxin response factors (ARFs) are an important family of auxin-mediated proteins that have key roles in various physiological and biochemical processes. The development of genomic data regarding Arabian jasmine provides the opportunity to annotate and classify the entire genome of this species and conduct comparative genomic studies.
During this study, the sequences of ARF genes in Arabian jasmine were identified via data mining of the existing genome and transcriptome. Furthermore, comprehensive analyses of the ARF gene structure, motif composition, cis-acting regulatory elements, and expression profiles in different tissues were performed. This work creates the foundation for the functional characterization of JsARF genes.
Jasminum is a genus comprising erect or climbing shrubs in the Oleaceae family, which includes ∼60 species in China that can be divided into single-leaved, double-leaved, and multi-petaled types. Arabian jasmine (Jasminum sambac) has high ornamental, economic, edible, and medicinal values. Most species are resistant to abiotic stress, and the deciduous vine is extremely hardy and drought-tolerant.
Auxin is widely distributed in plants and has an important role in plant growth and development, including seed germination, inflorescence formation, fruit development, leaf formation, and root structure formation and differentiation. Auxin can directly regulate the process of cell division, differentiation, and expansion through interactions with the recipient cell membrane or via other signaling pathways
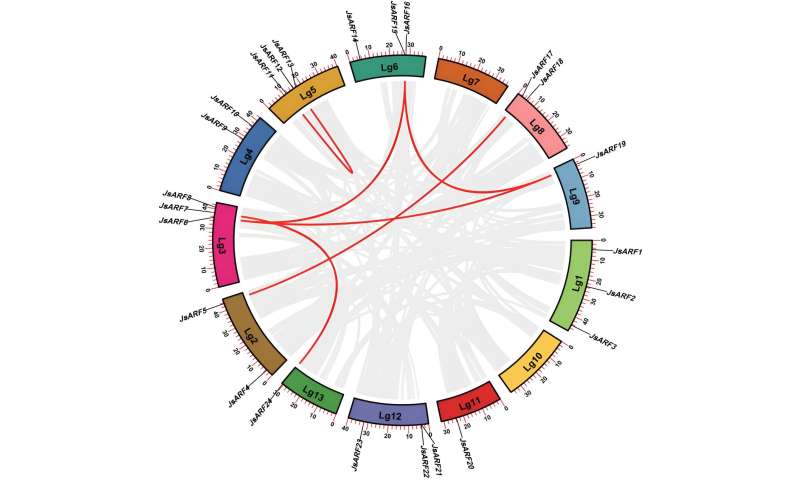
In the present study, 24 JsARF genes were identified in Arabian jasmine. The JsARF genes were randomly located on different chromosomes and divided into seven subfamilies according to a phylogenetic analysis of their encoded protein sequences. Their properties were analyzed using gene replication, expression profiles, cis elements, and protein–protein interaction networks. Different types of JsARF partners could interact with each other, and RNA-seq data revealed that most JsARF genes were expressed differently in different tissues.
JsARF5, JsARF12, and JsARF17 were strongly expressed in roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. These highly expressed genes might have important roles in plant growth. Additionally, the external application of IAA has an inhibitory or promoting effect on JsARF genes. Although the function of ARFs in Arabian jasmine is currently unknown, the expression profile and analysis of conserved motifs in this study can provide a valuable foundation for future research in this field.
More information:
Xin Huang et al, Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Auxin Response Factor Genes in Arabian Jasmine, Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science (2023). DOI: 10.21273/JASHS05276-22
Provided by American Society for Horticultural Science