Spin-locked effect in non-Euclidean space
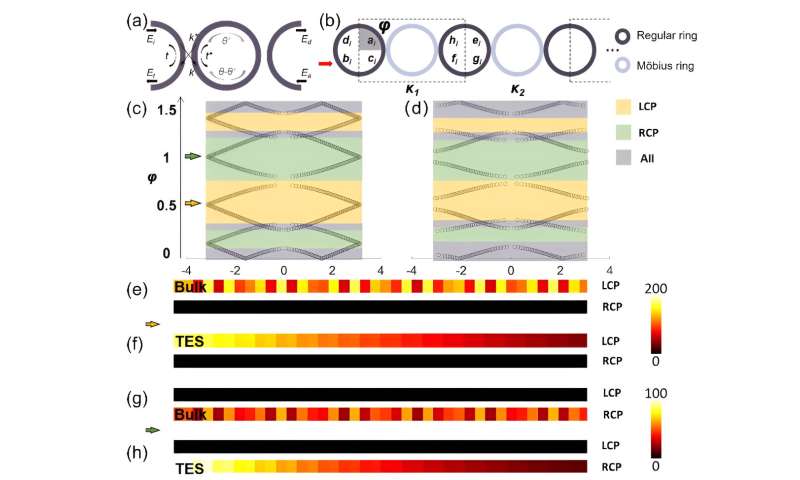
Modulation of topological phase transition has been pursued by researchers in both condensed matter and optics research fields, and has been realized in Euclidean systems, such as topological photonic crystals, topological metamaterials, and coupled resonator arrays. However, the spin-controlled topological phase transition in non-Euclidean space has not yet been explored.
In work, titled "Spin-controlled topological phase transition in non-Euclidean space" published in Frontiers of Optoelectronics, researchers propose a non-Euclidean configuration based on Möbius rings, and demonstrate the spin-controlled transition between the topological edge state and the bulk state.
The Möbius ring, which is designed to have an 8π period, has a square cross section at the twist beginning and the length/width evolves adiabatically along the loop, accompanied by conversion from transverse electric to transverse magnetic modes resulting from the spin-locked effect.
According to the authors, this work provides a new degree of polarization to control topological photonic states based on the spin of Möbius rings and opens a way to tune the topological phase in non-Euclidean space.
More information:
Zhuochen Du et al, Spin-controlled topological phase transition in non-Euclidean space, Frontiers of Optoelectronics (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s12200-024-00110-w
Provided by Frontiers Journals