Storage, form and influencing factors of karst inorganic carbon in a carbonate area in China
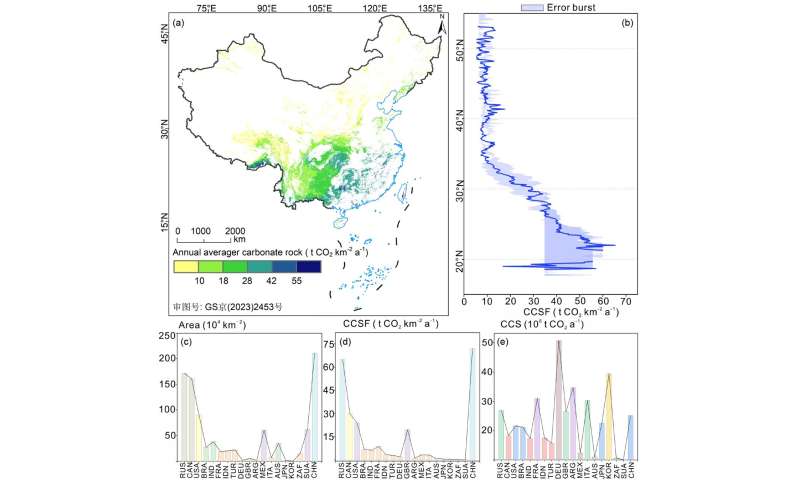
Carbonate rock chemical weathering carbon sinks reduce the rate of increase of the atmospheric CO2 concentration and global warming. Based on the river ion concentration data, the stochastic forest algorithm and the thermodynamic dissolution model quantify the CCSF of China from 1991 to 2020 to be 22.76 t CO2 km-2 a-1.
Among the countries with major global carbonate distributions, China's CCSF is second only to that of Russia (25.34 t CO2 km-2 a-1), is higher than those of the United States (17.53 t CO2 km-2 a-1), Brazil (16.76 t CO2 km-2 a-1), Canada (12.43 t CO2 km-2 a-1), and India (10.93 t CO2 km-2 a-1). It is also higher than the CCSF of Slovenia (7.59–16.50 t CO2 km-2 a-1), the average global CCSF (15.77 t CO2 km-2 a-1), and other countries with CCSF.
China's CCS is 4772.67×104 t CO2 yr-1, which is relatively low compared to the CCS in Canada (19946.7×104 t CO2), the United States (15924.3×104 t CO2), and France (5742×104 t CO2).
Although the area of carbonate rocks in China only accounts for 15.64% of the global carbonate rock area, it provides 14.91% of the karst carbon sinks in the global CCS (3.2×108 t CO2), and thus, it makes an important contribution to the achievement of China's and even global carbon neutrality goals.
The spatial distribution of CCSF in China shows a decreasing trend from southeast to northwest. The high value is 33.14 t CO2 km-2 a-1 in the southern karst area with high water and heat flux, and the low value is 7.27 t CO2 km-2 a-1 in the cold and dry northern karst area. In addition, in the climate division of Ke Ben, with the northward movement of the climate zone, CCSF shows a decreasing trend.
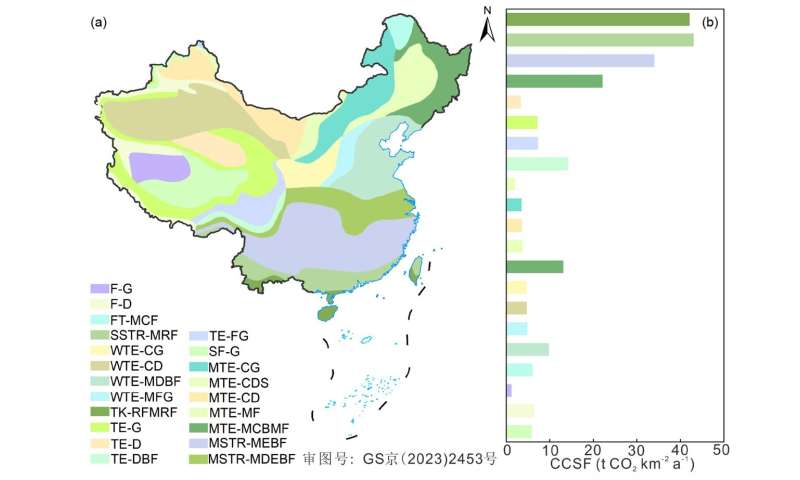
The distribution of carbonate rocks in tropical and subtropical areas is the most concentrated, and the hydrothermal conditions are the most abundant, with the highest CCSF of 42.99 t CO2 km-2 a-1. As the climate zone moves northward, the distribution area of carbonate rocks in the grassland climate zone with higher latitudes decreases, and the hydrothermal conditions are relatively weakened. The lowest CCSF is 1.17 t CO2 km-2 a-1.
There are also differences in CCSF formed by weathering of the three types of carbonate rocks, among which limestone is 21.51 t CO2 km-2 a-1 is 23.57 t CO2 km-2 a-1 and mixed rock is 25.59 t CO2 km-2 a-1.
The contribution rates of MAP, MAT, ET, NDVI, and SM to CCSF were 63.3%, 3.02%, 27.5%, 3.1%, and 3.05%, respectively. Among them, 95.40% of the areas are positively contributed by MAP and CCSF. That is, the increase in precipitation provides sufficient water conditions for carbonate weathering and accelerates the weathering process of carbonate rocks, with a contribution rate of 63.3%.
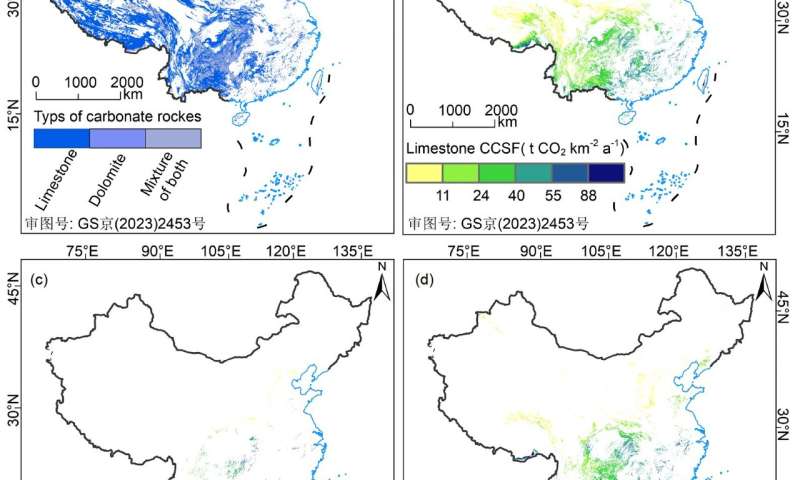
On the contrary, the negative contribution of evapotranspiration and CCSF is 88.97%, and its contribution rate is 27.5%; that is, evaporation is enhanced, which weakens the water supply for carbonate rock weathering, thus slowing down the weathering process of carbonate rocks.
The research is published in the journal Science China Earth Sciences.
More information:
Chaochao Du et al, Storage, form, and influencing factors of karst inorganic carbon in a carbonate area in China, Science China Earth Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s11430-023-1249-9
Provided by Science China Press