Weekly recaps

Recap / Best of Last Week—Nail polish dryers damage DNA, why batteries self-discharge, fixing high blood pressure
It was an interesting week for the study of human activities as a team at the University of California San Diego announced that UV-emitting nail polish dryers damage human DNA and cause mutations in cells—used to cure gel ...
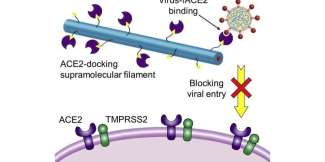
Recap / Best of Last Week—Record ocean temp set, new way to 3D print hydrogel electronics, nasal spray to ward off all viruses
A team of researchers from China, the U.S., Italy and New Zealand reported that ocean temperatures hit a new record high last year—the 10 zettajoule increase marked the hottest year ever recorded in the world's oceans. ...

Recap / Best of Last Week—Entangled beams of light, AI gadgets at CES 2023, good hydration linked to healthy aging
It was a good week for science research as a team at the University of São Paulo's Physics Institute's Laboratory for Coherent Manipulation of Atoms and Light developed a light source that produced two entangled beams of ...

Recap / Best of Last Week—Penguins may possess self-awareness, a new way to refrigerate, the huge expense of treating sepsis
It was a good week for biological research as a team of biologists from Czechia, Germany and Austria, discovered a type of bacteria that uses both bacteriochlorophyll-based photosynthetic complexes and proton-pumping rhodopsins ...

Recap / Best of Last Week—Fusion breakthrough, link between COVID and heart ailment, a lipid that plays a role in muscle aging
It was a good week for physics research as government officials in the U.S., including President Joe Biden, hailed the fusion breakthrough at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory as a milestone for mitigating climate ...

Recap / Best of Last Week—Turning a common plant into a weed, tapping water vapor over oceans, mapping sixth sense genes
It was an interesting week for planetary and Earth science as an international team of researchers discovered that intensive agricultural practices in North America over the past century have turned a wild plant into a pervasive ...
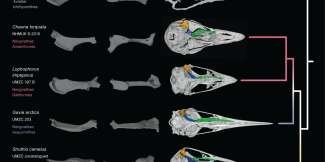
Recap / Best of Last Week—Overturning bird evolutionary theory, dangers of AI apps, mapping multiple diseases in one person
A pair of paleontologists, one with the University of Cincinnati, the other the University of Colorado Boulder, rebutted recent reports that mammoths went extinct later than thought. Joshua Miller and Carl Simpson pointed ...
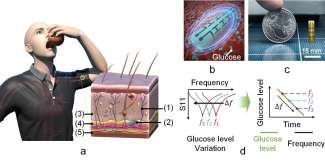
Recap / Best of Last Week—Cracking Emperor Charles' code, mimicking sleep in AI, measuring glucose without drawing blood
It was a good week for code cracking and the discovery of a biological enigma, as a team at the Loria research lab in eastern France cracked Emperor Charles V's secret code and uncovered a secret plot to kill the Holy Roman ...
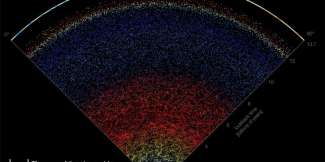
Recap / Best of Last Week—New map of universe, smart home vulnerabilities and young people at risk of hearing loss
It was a good week for space science as a team of astronomers at Johns Hopkins University created a new map of the universe that shows, for the first time, the span of the entire known cosmos. Also, NASA announced that its ...
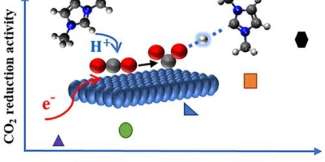
Recap / Best of Last Week—Cause of the first mass extinction, efficiently converting CO2 to CO, health dangers of vaping
A team of geobiologists at Virginia Tech found clues to Earth's first known mass extinction event 550 million years ago—evidence shows that its cause was tied to a global decrease in oxygen. Also, a pair of archaeologists, ...
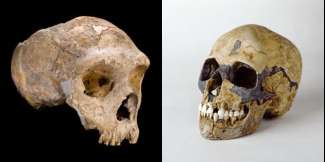
Recap / Best of Last Week—Neanderthals went extinct due to sex, using sunlight for WiFi, a vaccine for breast cancer
It was a good week for biological research as a team at the University of Toronto found that some degree of antibiotic resistance can be linked to household products—they found that triclosan was the predominant antibiotic ...
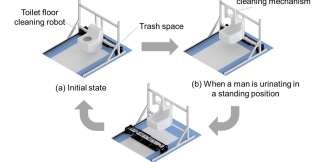
Recap / Best of Last Week—Alternate theory of gravity, automated restroom cleaning, Martian meteorite mystery solved
It was a good week for physics research as an international team of astrophysicists made observations of star clusters that were consistent with the predictions of an alternative theory of gravity—called "modified Newtonian ...